Backup Configuration
To configure the backup procedure, navigate to the "Backups" section from the root user's account.
Upon your first visit to this section, you will be able to specify the basic parameters for creating backups. In the future, you can manage them in the same section using the "Settings" option.
Choosing a Backup Storage Location
First, determine where you want to store your backups.

You can store copies on the server itself (local directory), in cloud storage, S3 storage, or on external servers by configuring the copy process via FTP/SFTP.
When choosing the local directory, backup archives will take up a specific amount of space on the server. However, this option is not the most reliable; in case of a critical server failure, you risk losing your data along with the created copies. It is recommended to set up copying to remote storage.
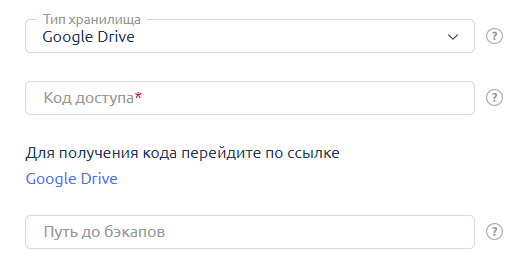
When selecting cloud storage (Dropbox, Google Drive), you will need to obtain an access code by following the link provided in the ISPmanager interface and specify the directory in which backup archives should be stored.
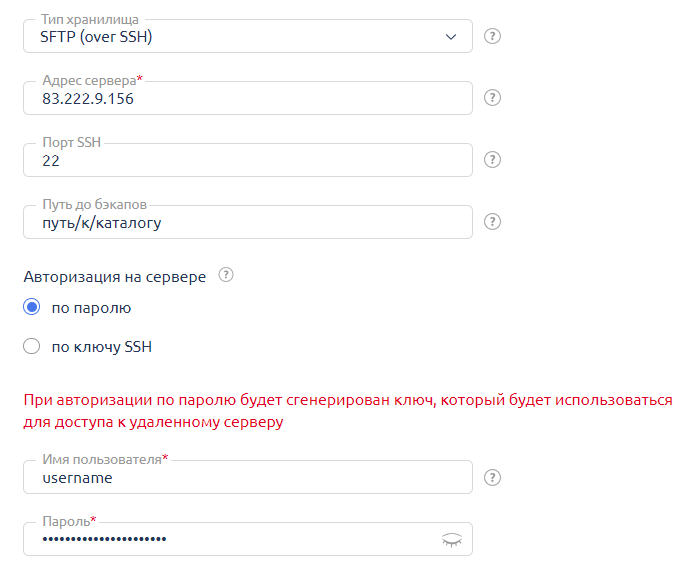
When choosing the FTP/SFTP option, you will need to specify the address of the remote server and select the authentication method: password (in this case, you need to specify the username and password) or using a key (in this case, you need to specify the username and their private key), as well as define the directory for storing backup copies.
Additional Settings
In the Limitations tab, you have the option to configure additional parameters such as exclusions from backup, the number of stored backup copies, and their maximum size.

If the set volume is reached, the system will automatically start deleting the oldest copies. Even if the limit is not set, but the free space in storage runs out, the system will also begin deleting old copies to free up space.
Here, you can also specify which files, folders, or even databases should be excluded from the backup procedure. Paths to files and folders should be specified relative to the user's home directory, e.g., /var/www/username/. For example, to exclude the directory /var/www/username/data/www/domainname/example from the copy, specify data/www/domainname/example.
It is often recommended to exclude temporary directories, caches, and test or temporary databases from the backup if their preservation is not necessary. To do this, simply specify their names in the respective field, one per line.
Backup Schedule
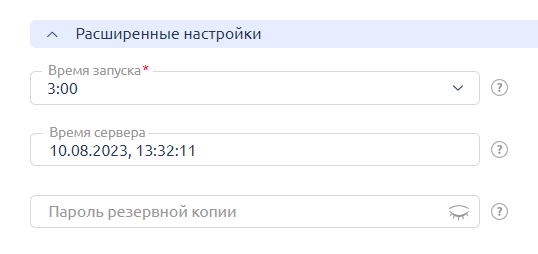
By default, backup is performed daily at 3 AM. The first full backup of the week is created on Sunday night, while all others are differentials containing only changes made over the past day.
You can change the backup schedule in the "Advanced Settings" section.
Restoring from a Backup
You have the option to download the created backup ("Backups" - select the desired copy - "Download") or perform a data restoration procedure.
Full Restoration
This process can be carried out on behalf of the root user. Go to the "Backups" section, double-click on the desired backup (or click "View Files"), then select the user from the list whose data was lost, and click the "Restore" button.

Selective Restoration
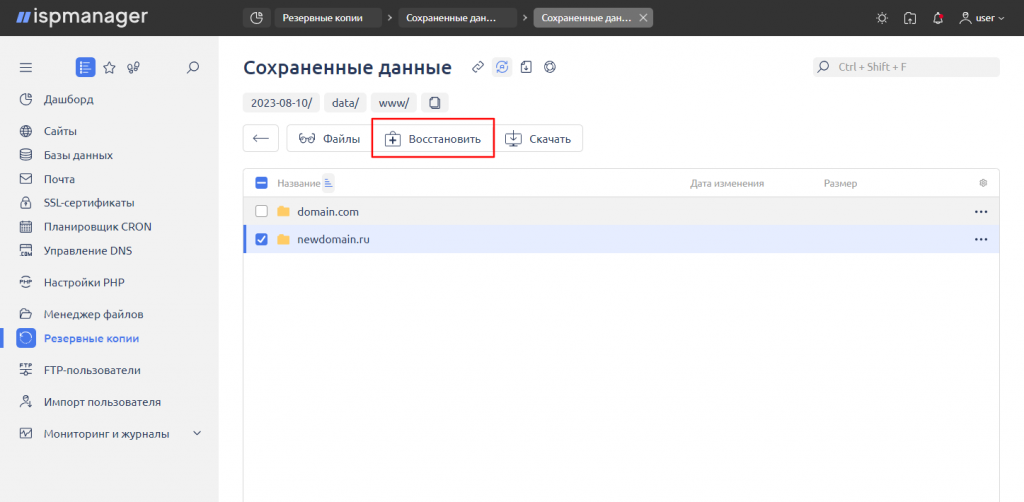
To restore only specific data, log into the control panel under the user's account and go to the "Backups" section.
Double-click on the backup for the desired date to access the list of saved data. This data is divided into types: Files, Databases. Select the desired type and double-click on it. This will take you to the list of saved directories and files (you can go further down several levels) or to the databases. Choose the necessary items for restoration and click the "Restore" button.